由于工作原因,最近比较深入的研究了Spring Cloud系列的产品,今天就来重点说说其中一个负责配置的产品 - Spring Cloud Config。
1. What is Spring Cloud Config?
其官方文档中对自己的定义是:
Spring Cloud Config provides server and client-side support for externalized configuration in a distributed system. With the Config Server you have a central place to manage external properties for applications across all environments.
简单来说,Spring Cloud Config就是我们通常意义上的配置中心 - 把应用原本放在本地文件的配置抽取出来放在中心服务器,从而能够提供更好的管理、发布能力。
另外,Spring Cloud Config提供基于以下3个维度的配置管理:
- 应用
- 这个比较好理解,每个配置都是属于某一个应用的
- 环境
- 每个配置都是区分环境的,如dev, test, prod等
- 版本
- 这个可能是一般的配置中心所缺乏的,就是对同一份配置的不同版本管理
- Spring Cloud Config提供版本的支持,也就是说对于一个应用的不同部署实例,可以从服务端获取到不同版本的配置,这对于一些特殊场景如:灰度发布,A/B测试等提供了很好的支持。
2. Why Spring Cloud Config?
那么大家可能会问了,配置中心现在不管是开源的,还是一些公司自己闭源投入使用的产品已经不少了,为啥还会诞生Spring Cloud Config呢?
在我看来,Spring Cloud Config在以下几方面还是有比较独特的优势,所以可能是为啥要再造一个轮子的原因吧:
- 基于应用、环境、版本三个维度管理
- 这个在前面提过了,主要是有版本的支持
- 配置存储支持Git
- 这个就比较有特色了,后端基于Git存储,一方面程序员非常熟悉,另一方面在部署上会非常简单,而且借助于Git,天生就能非常好的支持版本
- 当然,它还支持其它的存储如本地文件、SVN等
- 和Spring无缝集成
- 它无缝支持Spring里面
Environment和PropertySource的接口 - 所以对于已有的Spring应用程序的迁移成本非常低,在配置获取的接口上是完全一致的
- 它无缝支持Spring里面
3. Dive into Spring Cloud Config
相信大家看到这里,已经对Spring Cloud Config有了一个初步的认识,接下来我们就来深入了解下它吧~
3.1 Overview
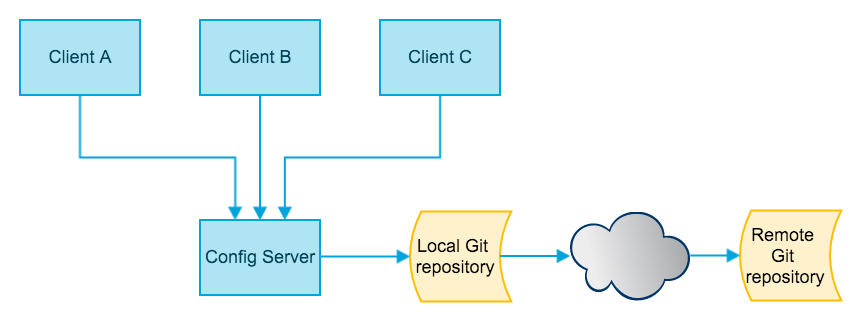
上图简要描述了一个普通Spring Cloud Config应用的场景。其中主要有以下几个组件:
- Config Client
- Client很好理解,就是使用了Spring Cloud Config的应用
- Spring Cloud Config提供了基于Spring的客户端,应用只要在代码中引入Spring Cloud Config Client的jar包即可工作
- Config Server
- Config Server是需要独立部署的一个web应用,它负责把git上的配置返回给客户端
- Remote Git Repository
- 远程Git仓库,一般而言,我们会把配置放在一个远程仓库,通过现成的git客户端来管理配置
- Local Git Repostiory
- Config Server的本地Git仓库
- Config Server接到来自客户端的配置获取请求后,会先把远程仓库的配置clone到本地的临时目录,然后从临时目录读取配置并返回
3.2 Demo
为了给大家一个比较直观的印象,我们通过一个简单的demo来看一下Spring Cloud Config是如何配置和使用的。 (完整的示例代码可以从 github 上获取到)
3.2.1 Remote Git Repository
首先我们准备一个远端的Git仓库,并且放入一个配置文件,下面是我使用的示例:
- Git仓库:git@github.com:nobodyiam/config-repo.git
- 配置文件:foo-production.properties,里面存放了一个foo的key,值为Hello World
- foo: Hello World
3.2.2 Config Server Demo
3.2.2.1 Maven依赖
Config Server Demo是一个基于Spring Boot的web应用,我们首先需要做的就是在pom中引入Spring Cloud Config Server的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0.M5</version>
</dependency>
3.2.2.2 Config Server配置
我们需要做一些配置使Config Server能从远端Git仓库获取配置信息,以下是application.yml中的配置,注意下面的spring.cloud.config.server.git配置。
spring:
application:
name: configserver
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: git@github.com:nobodyiam/config-repo.git
server:
port: 8888
3.2.2.3 启用Config Server
最后就是启用Config Server,只需要加上@EnableConfigServer即可。
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(ConfigServerApplication.class)
.run(args);
}
}做完以上配置后,启动应用,Config Server就开始工作了!
3.2.3 Config Client Demo
3.2.3.1 Maven依赖
Config Client Demo是一个基于Spring Boot的web应用,我们首先需要做的就是在pom中引入Spring Cloud Config Client的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-client</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0.M5</version>
</dependency>
3.2.3.2 Config Client配置
我们需要做一些配置使Config Client知道Config Server的地址,以及应用自身配置的信息,如:应用名字,环境,配置的版本等信息,以下是bootstrap.yml中的配置:
spring:
application:
name: foo
profiles:
active: production
cloud:
config:
uri: http://localhost:8888
label: master
3.2.3.3 应用读取配置
前面提到Spring Cloud Config的一大优势是和Spring无缝集成,所以应用侧在读取配置的时候和普通的Spring应用没有任何区别,只要通过Environment对象或者注入即可。
通过Environment对象
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public void doSomething() {
String configValue = env.getProperty("foo", "undefined");
// do more logic...
}通过注入
@Value("${foo}")
private String foo;做完以上配置后,启动应用,Config Client就会自动从Config Server获取配置,并无缝支持上面的应用读取配置场景!
3.3 Config Server实现细节
看了前面的demo,我们已经初步领略到了Spring Cloud Config的强大之处,通过短短几行配置就实现了分布式配置!
相信大家一定想了解Config Server是如何实现的吧,所以接下来我们继续Dive!
3.3.1 Config Server接口
Config Client通过Config Server提供的HTTP接口来获取数据,接口定义如下:
- URL:
/{application}/{profile}/{label} - Method: GET
- 参数说明
- application:应用名
- profile:环境
- label:版本
接口返回样例:
curl http://localhost:8888/foo/production/master
{
"name": "foo",
"profiles": ["production"],
"label": "master",
"version": "62cac1f5514358c4e3302c7ae07cd12db3deeeb6",
"propertySources": [{
"name": "git@github.com:nobodyiam/config-repo.git/foo-production.properties",
"source": {
"foo": "Hello World "
}
}]
}我们可以看到,返回的数据中,除了应用的名字,环境,版本和配置外,还有一个version字段,这个version就对应了git仓库上的commit hash。
3.3.2 Config Server实现细节
下图展示了Config Server的配置获取接口是如何读取到配置的。
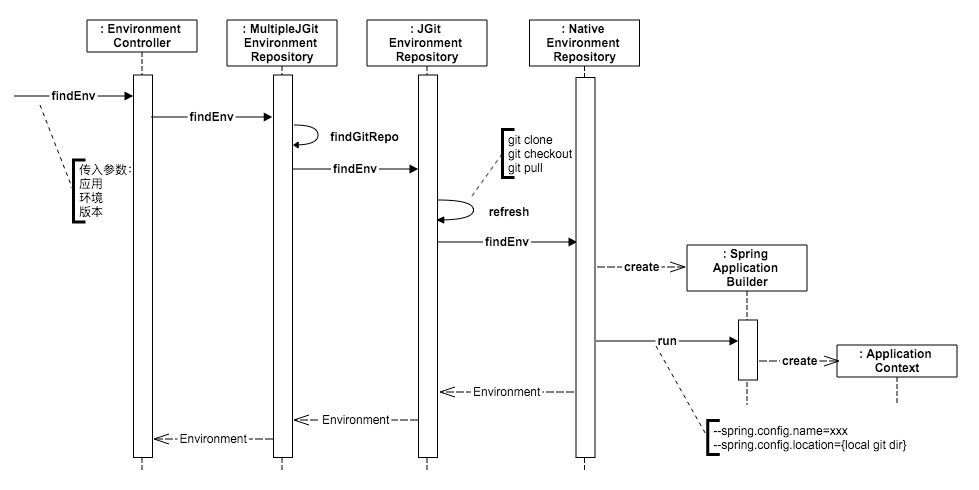
基本思路
- 根据客户端传过来的应用、环境信息找到对应Git Repository
- 在本地clone git repository,并切换到指定版本
- 创建一个Spring Application Context,指定这个ApplicationContext的名字为客户端传过来的应用名字,指定配置文件路径为本地git目录
- Spring在创建Application Context的过程中会到本地git目录,通过应用名字结合profile自动加载对应的配置文件信息
- 从创建出来的Spring Application Context中取出配置信息并返回给客户端
这个实现方式其实是挺讨巧的,它实际只是做了把远端的git仓库内容更新到了本地(从JGitEnvironmentRepository到NativeEnvironmentRepository),然后通过Spring Boot自身的配置加载逻辑获取配置信息。
3.4 Config Client实现
3.4.1 背景知识
在了解Config Client具体如何实现之前,我们先来重温一下Spring中的Environment和PropertySource。
- Environment
- Spring的ApplicationContext会包含一个Environment
- Environment自身包含了很多个PropertySource
- PropertySource
- 属性源
- 可以理解为很多个Key - Value的属性配置
在运行时的结构形如:
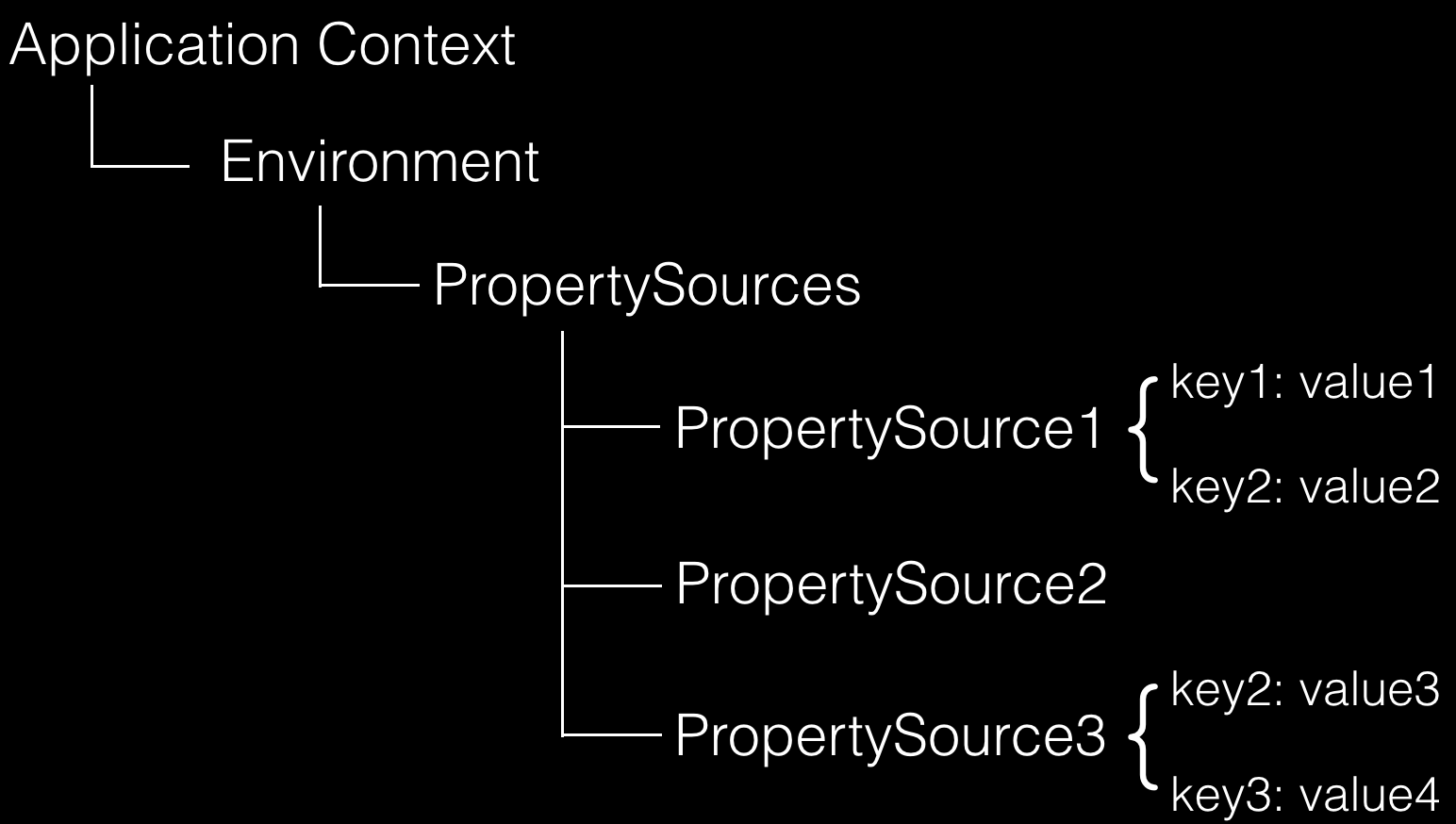
需要注意的是,PropertySource之间是有优先级顺序的,如果有一个Key在多个property source中都存在,那么在前面的property source优先。
所以对上图的例子:
- env.getProperty(“key1”) -> value1
- env.getProperty(“key2”) -> value2
- env.getProperty(“key3”) -> value4
3.4.2 Config Client实现细节
在有了相关背景知识后,我们来看看Spring Cloud Config Client的实现细节。
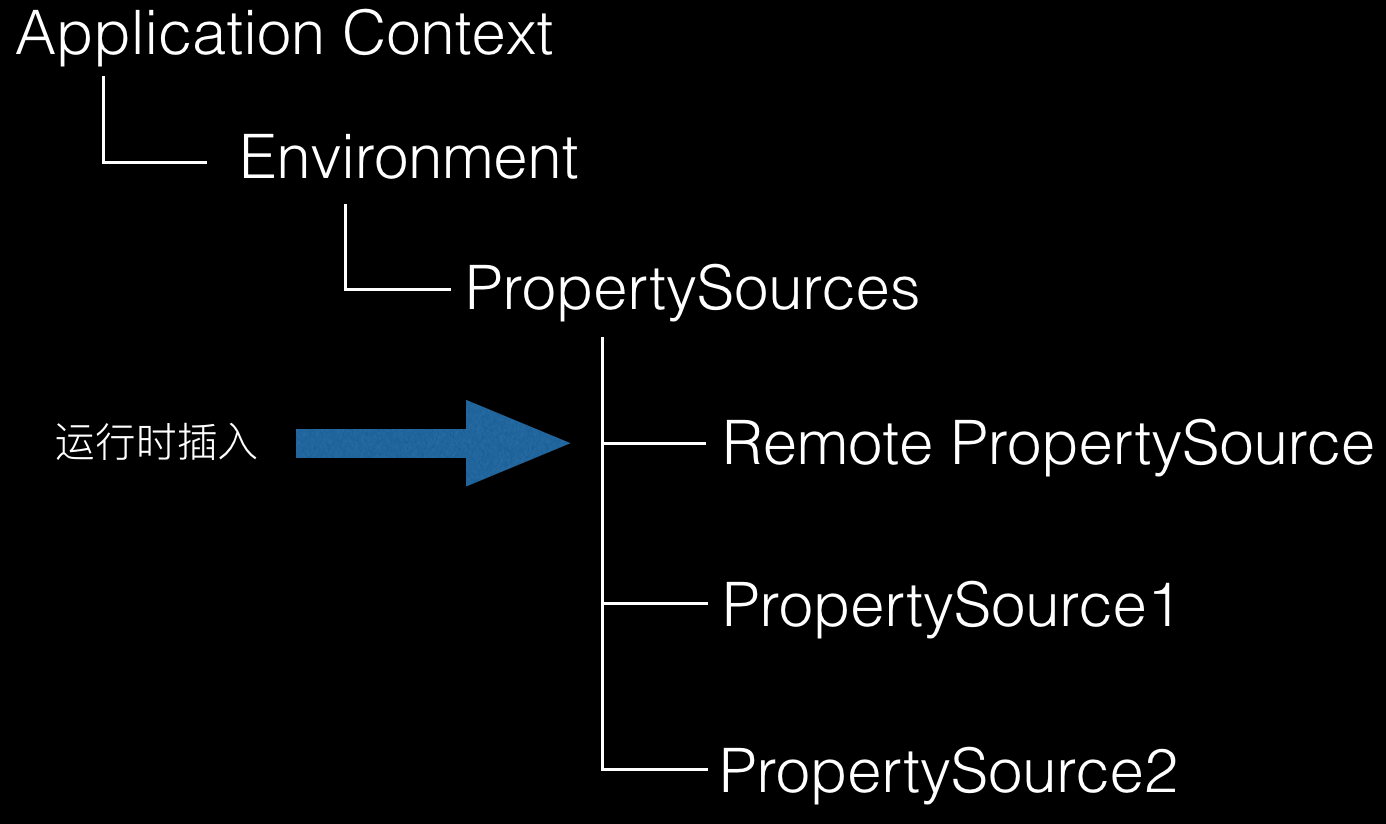
如上图所示,其实原理很简单,就是在应用启动阶段,从Config Server获取配置,然后组装成PropertySource并插入到第一个(这是默认行为,也可以配置成插入到特定位置)。
所以,在随后的获取配置过程中,来自Config Server的配置和其它本地的配置对使用者而言是没有任何差别的,从而实现了无缝集成。
3.5 配置更新实现
在了解了Config Server和Config Client是如何实现配置加载后,我们来看看对于配置更新的情况如何处理。
对于基于Git远程仓库的配置而言,配置更新可以分为3个阶段:
- Git提交更改配置文件
- Config Client感知到配置更改
- Config Client从Config Server获取到最新的配置,把最新的配置更新到环境中,并且更新已经注入的值
第一个步骤其实就是Git的更新流程,没啥好讨论的,所以下面主要介绍下第二步和第三步的实现思路。
3.5.1 Config Client感知到配置更改
这块其实Spring Cloud Config自己并没有提供原生的支持,不过提供了解决方案的建议:
- 很多git仓库提供了webhook的功能,如GitHub Webhooks。通过这个功能,当git仓库发生变化的时候,GitHub会发起一个请求到指定的URL,如Config Server。
- Config Server接收到变化的请求后,发出一个配置更新的消息
- Config Client接收到配置更新的消息,从而感知到配置更改
大致的流程如下图所示:
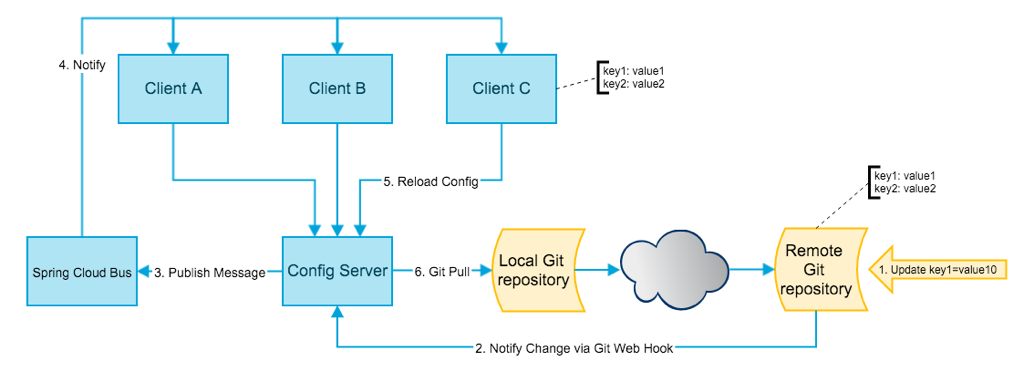
3.5.2 Config Client更新应用的配置
在Config Client感知到配置更改后,需要做两件事情:
- 从Config Server获取到最新的配置
- 更新环境中的配置,并更新Bean中已经注入的值
我们先来看一下Spring Cloud引进的一个新的bean scope - RefreshScope。
3.5.2.1 RefreshScope
我们知道Spring原生提供了一些scope,如singleton,prototype,request等。
为了实现配置更新后,已经注入bean的值也能更新的目的,Spring Cloud提供了一个新的scope - RefreshScope。
Spring Cloud对RefreshScope的定义如下:
A Scope implementation that allows for beans to be refreshed dynamically at runtime (see refresh(String) and refreshAll()). If a bean is refreshed then the next time the bean is accessed (i.e. a method is executed) a new instance is created.
所以,对于那些有注入值的bean,我们可以把它们标记为RefreshScope,这样当运行时发现有配置更新的时候,通过调用RefreshScope.refresh(beanName)或RefreshScope.refreshAll(),从而下次这些bean被使用时会被重新初始化,进而会被重新注入值,所以也就达到了更新的目的。
代码示例:
@RefreshScope
public class FooTest {
@Value("${foo}")
private String foo;
public String getFoo() {
return foo;
}
}3.5.2.2 Config Client更新配置实现
最后我们来看看Spring Cloud Config Client是如何实现配置更新的:
基本思路
- Config Client从Config Server获取到最新的配置
- Config Client把最新的配置更新到当前Application Context
- 调用
RefreshScope.refreshAll方法 - 所有标记
@RefreshScope的bean都会在下次调用时重新初始化
4. Summary
本文主要介绍了Spring Cloud Config的实现思路,可以看到尽管Spring Cloud Config是一个比较小的项目,不过实现思路还是有不少地方是值得我们去借鉴的,比如它简单的API、精简的配置、借助已有的实现来完成功能等。
另外,Spring Cloud Config产品本身也是比较适合应用在一些比较小的项目中,毕竟配置、存储都非常简单,部署也非常快。
不过我们也需要看到,如果希望把Spring Cloud Config作为一个基础服务应用到规模较大的公司去的话,还是有不少问题是需要克服的,比如git仓库的可用性、扩展性,Config Server的性能,配置更新的实时性等。
最后,瑕不掩瑜,Spring Cloud Config还是非常值得我们去学习和使用的!
